GAM이란?
Generalized Additive Models (GAMs) are a type of statistical model that extend Generalized Linear Models (GLMs) by allowing the linear predictor to be a sum of smooth functions of the predictor variables. This flexibility makes GAMs highly effective for capturing non-linear relationships between predictors and the response variable.
GLM의 연장선이며 smooth function을 추가해 독립변수와 종속변수 간의 non-linear한 관계도 capture 할 수 있게 해주는 모델이다. GLM과 GAM 모두 모델 분석 과정 중 각 독립변수가 종속변수에 기여하는 계수값들이 도출되므로 Interpretable Machine Learning이라고 할 수 있을 것이며, 이는 Decision Making에 매우 중요하다고 할 수 있다.

GAM을 이용해서 더욱 더 디테일한 데이터의 경향성을 찾아낼 수 있다.
GLM과의 차이점
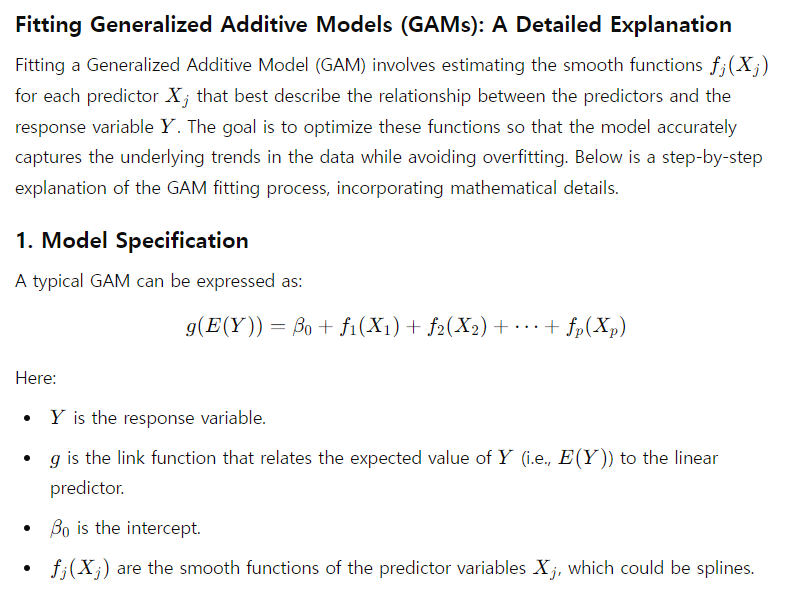
다음은 GLM의 모델 형태이다.
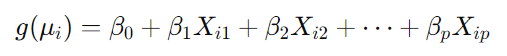
다음은 GAM의 모델 형태이다.


독립변수들에 smooth function들이 씌워진 채로 더해졌다고 볼 수 있다.
여기서 X_1 , X_2 등은 다음과 같은 뜻이다.

여기서 smooth라는 것은 Non-Linear 하다는 뜻이다.
Linear함과 Non-linear함은 다음과 같은 차이를 가진다.

Smooth function의 예시로는 spline이 있을 수 있다.
Splines are a type of smooth function used in statistical modeling to approximate complex relationships between variables. A spline is essentially a piecewise polynomial function that is defined over different segments of the predictor variable's range.
이 spline을 이용해서 독립/종속변수 사이의 non-linear한 relationship을 모델링할 수 있는 것이다.

이러한 smooth function들은 모델 업데이트를 통해 점차 조정되어간다.

그래서 GAM이 무엇인가?
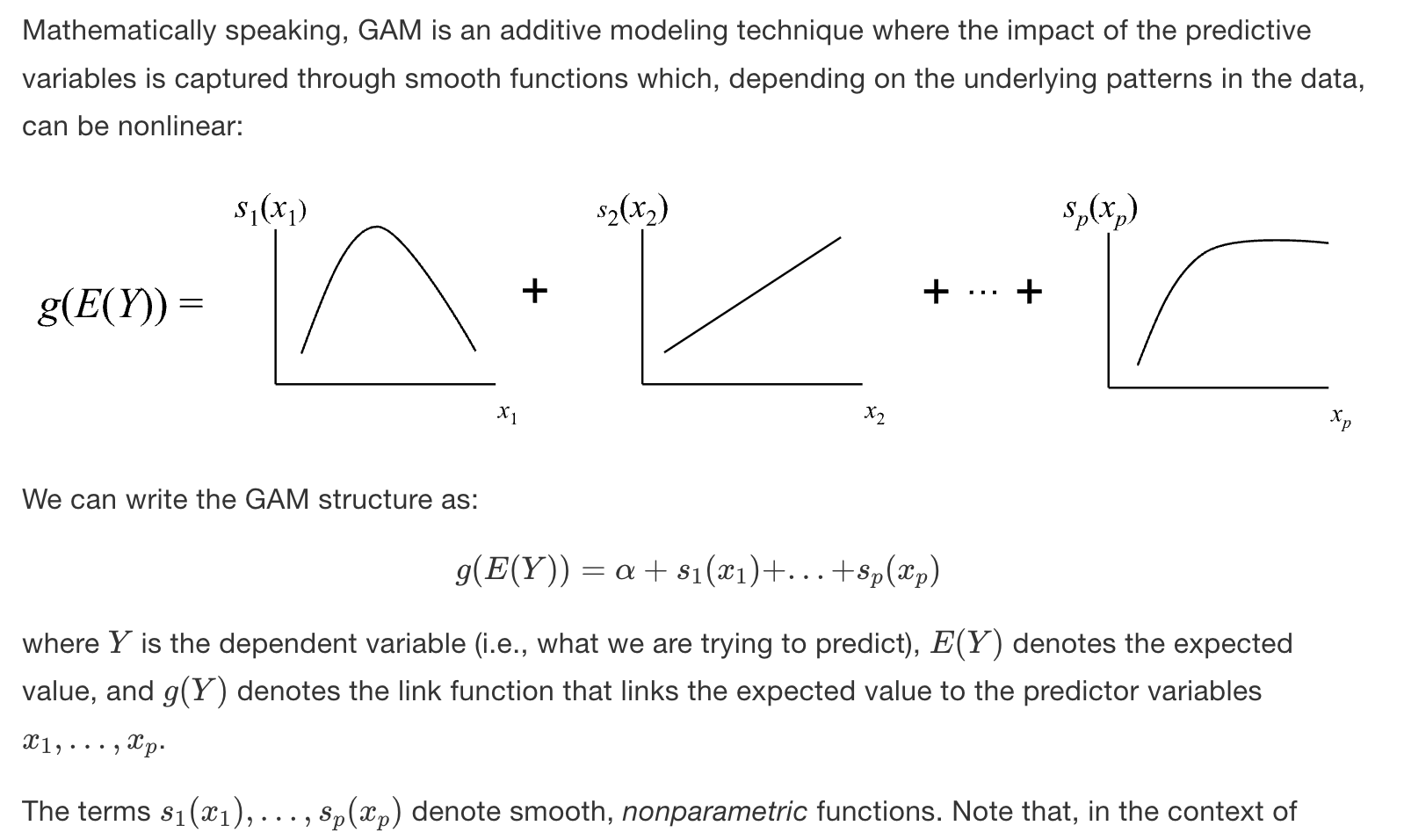
smooth, nonparametric function들을 다 더해서 데이터에 맞게 모델링 하는 기법인 것 같다. 여기서 nonparametric이란,
the terminology nonparametric means that the shape of predictor functions are fully determined by the data as opposed to parametric functions that are defined by a typically small set of parameters.
GLM에서는 각 predictor variable들의 계수를 추정하는 방식으로 해석가능한 모델을 만들어낸다.
GAM에서는 각 predictor variable들이 영향을 미치는 정도를 함수로 나타낸다.
다음은 Wage(월급)에 영향을 미치는 predictor variable(Year, Age, Education)의 effect을 GAM 모델링한 결과이다.

점선은 uncertainty를 나타낸다.
Why use GAMs?

다만 additive하다는 GAM의 가정은 반대로 GAM의 limitation이기도 하다.
부록: Fitting Generalized Additive Models (GAMs)
다음은 GAM이 smooth function들을 어떻게 데이터에 맞게 optimize하는지에 대한 과정이다.